Chart of Accounts
Introduction to Chart Of Accounts
A Chart of Accounts (COA) is an organizational tool that serves as an index of all the financial accounts in a company's general ledger. It categorizes and lists every account by line item, reflecting all the financial transactions that a company conducted during a specific accounting period. The COA is structured to display information in the order it appears in financial statements, starting with balance sheet accounts followed by income statement accounts. This structure helps in organizing finances and provides a clear view of the company's financial health to interested parties, such as investors and shareholders.
The COA can be tailored to fit the size and type of business, ensuring that it remains a relevant and useful tool for financial management and reporting. One of the following COA structures are used, depending on the organization's needs:
- Flat Chart of Accounts: This is a simpler structure where accounts are listed sequentially without further subdivision. It's typically used by smaller organizations with less complex accounting needs. In a flat COA, each account is usually represented by a unique number or code, and there are no additional layers or segments within the account structure.
- Segmented Chart of Accounts: This structure is more complex and is used by larger organizations that require detailed tracking and reporting. A segmented COA breaks down accounts into multiple segments or dimensions, such as department, location, or project. Each segment can have its own set of codes, allowing for a more granular and detailed categorization of financial transactions. This facilitates more sophisticated reporting and analysis, as it enables filtering and sorting of financial data across different segments of the organization.
Chart of Accounts Listing Screen
Ribbon Select Chart of Accounts - Chart of Accounts
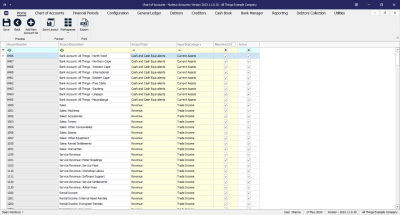
- The Chart of Accounts Listing screen will be displayed.
- Account Number: Is a unique multi-digit numeric code assigned to each financial account within a company's general ledger. This numbering system is designed to categorize and identify accounts easily, facilitating the organization, recording, and reporting of financial transactions.
- Account Description: A brief narrative that explains the purpose or nature of a specific account within the general ledger. It provides clarity on what types of transactions should be recorded in that account, ensuring accurate and consistent financial reporting. This description helps users of the financial statements, like accountants and auditors, to quickly understand the financial activities represented by each account.
- Account Type: This refers to the broad classification within the Chart of Accounts that organizes financial transactions. Account types are the main categories under which accounts are grouped, such as assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses. Each account type is designed to reflect a specific aspect of the business's financial situation and is used to structure the general ledger for systematic recording and reporting.
- Reporting Category: A reporting category typically refers to a more detailed sub-classification within the account types. Reporting categories are used to further break down account types into smaller segments for more granular financial analysis and reporting. They help in creating detailed financial reports and can be tailored to meet specific management or regulatory reporting requirements.
- Allow Direct Journals: This option lets you choose which accounts you can use for entering journal entries. This way, you can avoid using accounts that shouldn't be used for this purpose, like control accounts that are managed automatically.
- Active: This shows you whether the account is currently Active or not, and gives you the option to activate or deactivate the account as required. You can only carry out financial transactions with accounts that are currently active.
Action Buttons
Process
From this screen, you can:
- Save changes made to the Chart of Accounts.
- Add a New Account Number.
Format
- Save Layout - Saves any changes made to the data grid, such as changing column width.
- Workspaces - Saves layout preferences.
- Export - Click this to transfer all data from the current grid view into an MS Excel spreadsheet.
ACCT.COA.COA.Intro